Introduction
France is a country that occupies a significant portion of the western part of Europe, stretching from the English Channel or la Manche, in the north, to the Mediterranean Sea in the south. With an area of approximately 643,801 square kilometers, France is the largest country in the European Union. Known for its rich history, diverse culture, and stunning landscapes, France has played an important role in shaping Europe and the world.
France was Europe’s first modern republic, established during the French Revolution in the late 18th century, ultimately leading to the monarchy’s end and a new era of democracy. The country has since undergone several changes, including establishing the Fifth Republic in 1958, which has helped solidify France’s status as a leading industrial power.
France is renowned for its advanced manufacturing capabilities, innovative technologies, and highly skilled workforce, particularly in aerospace, telecommunications, and pharmaceuticals. The country is also known for its rich cultural heritage, which attracts millions of tourists each year, making it one of the most visited countries in the world. While there have been challenges and setbacks, France remains a global leader in business, technology, and culture, with a bright future ahead.
Jump to Introduction, Geography, Climate, People & Society, Economy, Insight, Google Maps, Facts, and Did You Know about France. Or visit the driving directions page for routing instructions.
Geography
France is a country of varied natural landscapes, with the northern half characterized by broad plains that spread across the landscape. These plains are known for their fertile soils, making them ideal locations for agriculture and farming.
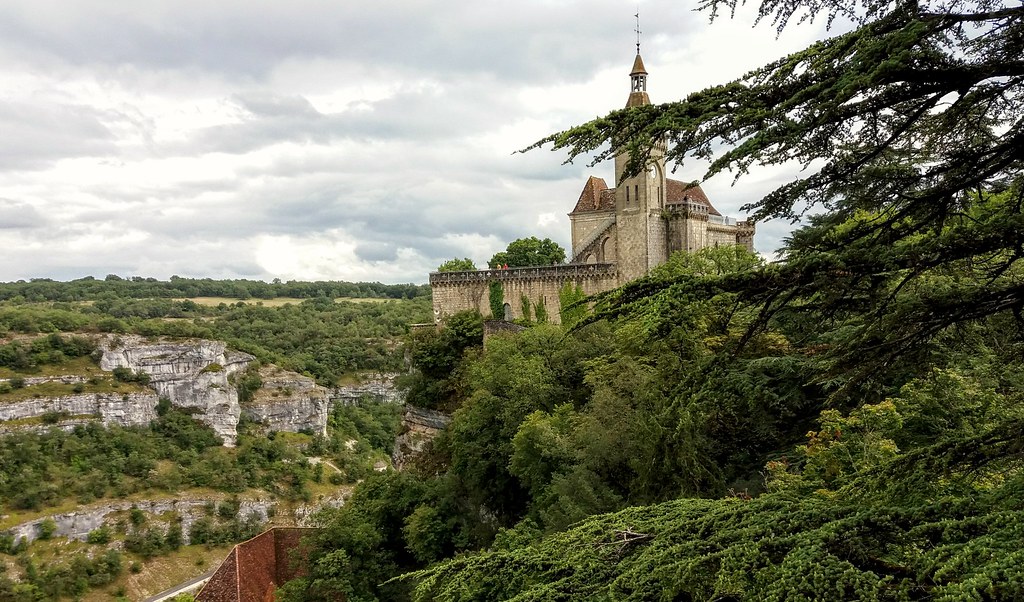

In contrast, the eastern and southwestern regions of the country are dominated by high mountain ranges. The Alps, which stretch along France’s southeastern border, are one of the most prominent mountain ranges in the world, featuring towering peaks and breathtaking vistas. In the Pyrenees, which form the natural boundary between France and Spain, rugged cliffs, deep valleys, and majestic forests create a unique and stunning landscape.
Between the mountain ranges lies a plateau region known as the Massif Central, home to various geological features, including volcanic peaks, deep gorges, and rolling hills. This region is also characterized by its vast forests, including the Cévennes and the Montagne Noire, home to many plant and animal species.
In addition to its stunning natural landscapes, France has a rich cultural heritage, with historic sites, museums, and art galleries throughout the country. From the Gothic architecture of Notre Dame de Paris to the vineyards of Burgundy, France has something to offer everyone, making it a popular destination for tourists worldwide.
Climate
France has diverse climates shaped by its geography and location in Western Europe. France has three main climate regions, each with unique characteristics and weather patterns.
The climate in the country’s northwest is generally temperate and damp, with cool summers and mild winters. This region, which includes cities such as Paris, is known for its frequent rainfall, which provides lush green vegetation and fertile soils. The cooler temperatures and mild weather make the region ideal for outdoor activities such as hiking, cycling, and sightseeing.
The eastern part of France experiences a continental climate, with hot summers and cold winters. This region, which includes major cities such as Strasbourg and Lyon, is characterized by its distinct seasons and extreme temperature fluctuations. The region is also home to numerous vineyards producing famous wines like Pinot Noir, Chardonnay, and Riesling.
The climate in the south of France is Mediterranean, with hot, dry summers and mild, rainy winters. This region, which includes popular tourist destinations such as Marseille, Nice, and Cannes, is renowned for its sunny beaches, beautiful coastal towns, and vibrant markets. The mild winters and warm summers make it an ideal location for year-round tourism, and the region is known for producing excellent olive oils and wines.
France’s diverse climate regions offer a unique blend of natural beauty, cultural heritage, and outdoor adventure opportunities, making it a popular destination for visitors worldwide.
People & Society
France is a country with a strong national identity that is deeply rooted in its history and culture. Despite this, the country also has pronounced regional differences, seen in the diversity of local customs, traditions, and even languages. While French is the country’s official language, many regional dialects and languages are spoken throughout France, including Breton, Occitan, and Alsatian.
Since the 1970s, France has tightened its immigration laws to control the number of people entering the country. This has led to tensions between immigrant populations and the larger French society, particularly in urban areas. Ethnic minorities growing up in city suburbs often feel increasingly alienated from the mainstream culture and excluded from opportunities for education and employment.
To promote national unity and discourage religious extremism, the French government banned wearing the veil in public in 2011. This has been a controversial topic, with some arguing that it infringes on religious freedom and others pointing to it as a necessary measure to protect secular values.
The issue of equality is also a topic of debate in France, with many arguing that more needs to be done to address issues of discrimination and social inequality. Recent changes to French law now require companies to disclose gender pay disparities and aim to increase the representation of women in positions of power. However, some critics argue that more needs to be done to address systemic discrimination within French society.
Despite these challenges, France remains a vibrant and diverse country with a rich cultural heritage and a commitment to social justice. As debates about immigration, equality, and national identity continue, the country remains a place of great importance both within Europe and on the global stage.
The Economy
France is a major economic power with a diversified export sector that includes chemicals, electronics, heavy engineering, cars, and aircraft. These industries are known for their high-quality products and cutting-edge technology, making French exports in demand worldwide. With a focus on innovation and efficiency, these sectors continue to grow and contribute to the country’s economic success.
In addition to these traditional industries, France is a world leader in cosmetics, perfumes, and quality wines. These industries have a rich history in France, and the country’s reputation for producing the finest luxury goods attracts millions of visitors annually. The cosmetics and perfume industry has a long-standing tradition of excellence. French brands such as Chanel, Dior, and Yves Saint Laurent are recognized worldwide for their quality and innovation.
French agriculture has also undergone significant modernization recently, adopting new technologies and practices to increase efficiency and productivity. France is now one of the world’s largest agricultural producers, with crops including wheat, corn, and barley and livestock such as cattle, sheep, and pigs. The country’s commitment to sustainable agriculture has increased demand for organic and locally produced foods, adding to the growing diversity of the agriculture sector.
The French economy is characterized by its diversity and strength, focusing on innovation, quality, and sustainability. As the country adapts and evolves, it remains an integral part of the global economy, driving growth and progress in fields ranging from technology to luxury goods.
Insight
France is undoubtedly one of the world’s most iconic and popular tourist destinations, attracting over 80 million visitors annually. France has something to offer everyone: rich cultural and historical attractions, stunning natural landscapes, beautiful cities, and world-renowned cuisine.
One of France’s main draws for tourists is its rich cultural heritage, displayed in its numerous museums, art galleries, and historic landmarks. The Louvre, located in Paris, is one of the most famous museums in the world, housing a vast collection of art and artifacts from throughout history. Other popular destinations include the Palace of Versailles, the Eiffel Tower, the Pont du Gard, and the Château de Chambord.
In addition to its cultural attractions, France is home to some of Europe’s most beautiful natural landscapes. With their snow-capped peaks and pristine alpine lakes, the French Alps draw millions of visitors yearly for skiing, snowboarding, and mountain climbing. The beaches of the French Riviera are also a major attraction, with their warm water and golden sands attracting sun-seekers from all over the world.
Food and wine are also an important part of French culture, with the country renowned for its haute cuisine and winemaking traditions. From Michelin-starred restaurants to cozy bistros, France offers many dining options that showcase the country’s culinary excellence.
France’s popularity as a tourist destination is a testament to its beauty, vibrancy, and rich cultural heritage. As one of the most visited countries in the world, it continues to inspire awe and wonder in travelers from all corners of the globe.
Google Maps
Facts
Name: France (French Republic), local name: Republique Francaise
Languages: French (official language) 100%, declining regional dialects and languages (Provencal, Breton, Alsatian, Corsican, Catalan, Basque, Flemish, Occitan, Picard);
ISO code: fr, internet: metropolitan France: .fr, French Guiana: .gf, Guadeloupe: .gp, Martinique: .mq, Mayotte: .yt, Reunion: .re
Capital city: Paris, GPS: 48 52 N, 2 20 E
Time: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time) (+1hr, begins last Sunday in March; ends last Sunday in October)
Population: 68,521,974 (2023 estimate). Note: the above figure is for metropolitan France and five overseas regions; the metropolitan France population is 62,814,233 (French / Frenchman (men), Frenchwoman (women))
Urban population: 81.2% (2021) – 11.079 million, Paris (capital city), 1.734 million, Lyon, 1.614 million, Marseille-Aix-En-Provence, 1.068 million, Lille, 1.037 million, Toulouse, 980,000 Bordeaux (2021)
Location: Metropolitan France: Western Europe, bordering the Bay of Biscay and the English Channel, between Belgium and Spain, southeast of the UK, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, and between Italy and Spain. Metropolitan France is a European country. You may find 47 other countries on this continent.
French Guiana: Northern South America, bordering the North Atlantic Ocean, between Brazil and Suriname.
Guadeloupe: Caribbean islands between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, southeast of Puerto Rico.
Martinique: Caribbean island between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, north of Trinidad and Tobago.
Mayotte: Southern Indian Ocean, an island in the Mozambique Channel, about halfway between northern Madagascar and northern Mozambique.
Reunion: Southern Africa, an island in the Indian Ocean, east of Madagascar.
Coordinates: Metropolitan France: 46 00 N, 2 00 E. French Guiana: 4 00 N, 53 00 W. Guadeloupe: 16 15 N, 61 35 W. Martinique: 14 40 N, 61 00 W. Mayotte: 12 50 S, 45 10 E. Reunion: 21 06 S, 55 36 E.
Bordering countries: (8 nations): Andorra 55 km, Belgium 556 km, Germany 418 km, Italy 476 km, Luxembourg 69 km, Monaco 6 km, Spain 646 km, Switzerland 525 km
Land area: 640,427 sq km. Metropolitan France: 549,970 sq km
Water area: 3,374 sq km; 1,530 sq km (metropolitan France)
Total area: 643,801 sq km. Metropolitan France: 551,500 sq km – Slightly more than four times the size of Georgia; slightly less than the size of Texas.
Terrain: Metropolitan France: mostly flat plains or gently rolling hills in the north and west. The remainder is mountainous, especially the Pyrenees in the south and the Alps in the east. French Guiana: low-lying coastal plains rising to hills and small mountains. Guadeloupe: basse-terre is volcanic in origin with interior mountains. Grande-Terre is a low limestone formation. Most of the seven other islands are volcanic in origin. Martinique: mountainous with an indented coastline and a dormant volcano. Mayotte: generally undulating, with deep ravines and ancient volcanic peaks. Reunion: mostly rugged and mountainous, fertile lowlands along the coast.
Highest point: Mont blanc 4,810
Lowest point: Rhone River delta -2 m
Major rivers: Rhine (shared with Switzerland, Germany, and Netherlands) – 1,233 km, Loire – 1,012 km
Natural hazards: Metropolitan France: flooding, avalanches, midwinter windstorms, drought, forest fires in the south near the Mediterranean. Overseas departments: hurricanes (cyclones), flooding. Volcanism: Montagne Pelee (1,394 m) on the island of Martinique in the Caribbean is the most active volcano of the Lesser Antilles arc; it last erupted in 1932; a catastrophic eruption in May 1902 destroyed the city of St. Pierre, killing an estimated 30,000 people; La Soufriere (1,467 m) on the island of Guadeloupe in the Caribbean last erupted from July 1976 to march 1977; these volcanoes are part of the volcanic island arc of the lesser antilles that extends from saba in the north to Grenada in the south.
National holiday(s): Fete de la Federation, 14 July (1790)
Did you know about France?
- France has the most time zones of any country worldwide, with 12 different time zones. This is due to its territories and dependencies spread across different continents.
- The French consume the most cheese per capita of any country globally, with over 1,200 varieties produced in France.
- The world’s first public transportation system, a horse-drawn carriage called a “carrosse à cinq sols,” was established in Paris in 1662.
- The French Revolution, which lasted from 1789 to 1799, resulted in the execution of the French king, Louis XVI, and the establishment of the First French Republic.
- The tallest bridge in the world, the Millau Viaduct, is in France. It spans over the Tarn River valley and is over 1,100 feet (343 meters) tall.
You may also be interested in Andorra, Belgium, Germany, Italy, Luxembourg, Monaco, Spain, and Switzerland.
Do you like this France-related maps & fact page? Please don’t forget to share with others!